View source
Download
.ipynb
Convert Semantic to Instance Segmentation¶
Transform a semantic segmentation dataset into instance segmentation format by separating individual object instances within each semantic class.
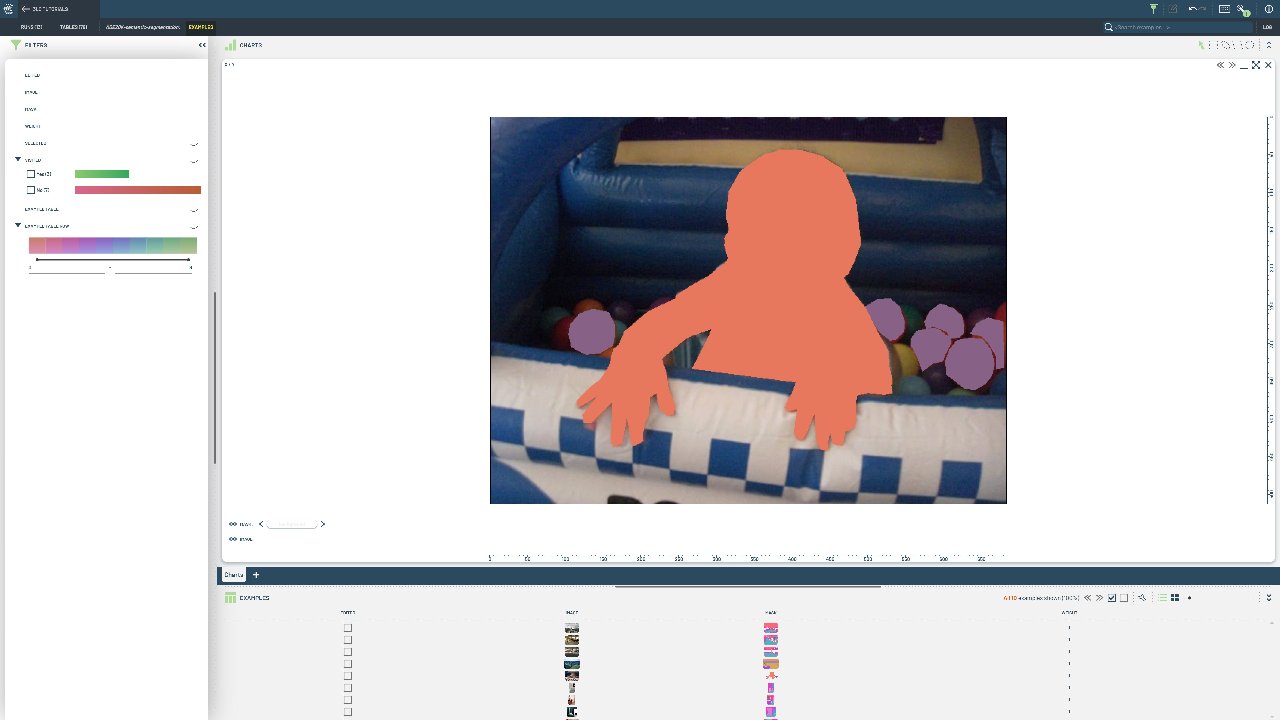
Semantic segmentation provides class labels but doesn’t distinguish between individual objects of the same class. Converting to instance segmentation enables counting objects, tracking individual instances, and performing more detailed analysis.
This notebook demonstrates converting semantic segmentation masks to instance segmentation by identifying connected components within each semantic class. We separate touching objects and create individual instance masks from the original semantic labels.
Project Setup¶
[ ]:
PROJECT_NAME = "3LC Tutorials - Create Tables"
DATASET_NAME = "ADE20k_toy_dataset"
DOWNLOAD_PATH = "../../transient_data"
Install dependencies¶
[ ]:
%pip install 3lc
%pip install huggingface-hub
%pip install git+https://github.com/3lc-ai/3lc-examples.git
%pip install matplotlib
Imports¶
Download the dataset¶
Fetch the label map from the Hugging Face Hub¶
Load the images and segmentation maps¶
[ ]:
[ ]:
# Call .to_relative() to ensure aliases are applied
image_paths = [tlc.Url(p).to_relative().to_str() for p in image_paths]
print(image_paths[0])
Transform the segmentation maps to instance segmentation masks¶
[ ]:
def single_channel_map_to_per_class_masks(map: np.ndarray) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""Convert a single channel segmentation map to a stack of per-class masks.
Args:
map: A numpy array of shape (H, W) representing a single channel segmentation map.
Returns:
A tuple of two numpy arrays:
- The first array is a stack of per-class masks of shape (H, W, N), where N is the number of classes in the map.
- The second array is a numpy array of shape (N,) representing the class IDs present in the map.
"""
masks = []
labels = []
for class_id in np.unique(map):
mask = (map == class_id).astype(np.uint8)
masks.append(mask)
labels.append(class_id)
return np.stack(masks, axis=-1), labels
[ ]:
# Build the column of instance segmentations in the format required by 3LC
mask_dicts = []
for mask_path in segmentation_map_paths:
map_np = cv2.imread(mask_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
h, w = map_np.shape
masks, labels = single_channel_map_to_per_class_masks(map_np)
mask_dicts.append(
{
"image_height": h,
"image_width": w,
"masks": masks,
"instance_properties": {
"label": labels,
},
},
)
Write the instance segmentation masks to a table¶
[ ]:
table_writer = tlc.TableWriter(
table_name="ADE20K-instance-segmentation",
dataset_name=DATASET_NAME,
project_name=PROJECT_NAME,
column_schemas={
"image": tlc.ImageUrlSchema(),
"instances": tlc.SegmentationSchema(
label_value_map={i: tlc.MapElement(v) for i, v in enumerate(categories)},
sample_type=tlc.InstanceSegmentationMasks.sample_type,
),
},
if_exists="rename",
)
[ ]:
# Add all rows (images and instance segmentations) to the table in one go
table_writer.add_batch(
{
"image": image_paths,
"instances": mask_dicts,
}
)
[ ]:
Visualize a sample instance segmentation mask¶
[ ]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
example_mask = table[0]["instances"]["masks"][:, :, 0]
plt.imshow(example_mask, cmap="gray")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()