.ipynb
Create Custom Keypoints Table¶
Create a 3LC keypoints table from the Animal-Pose dataset with custom schema definitions for pose estimation tasks.
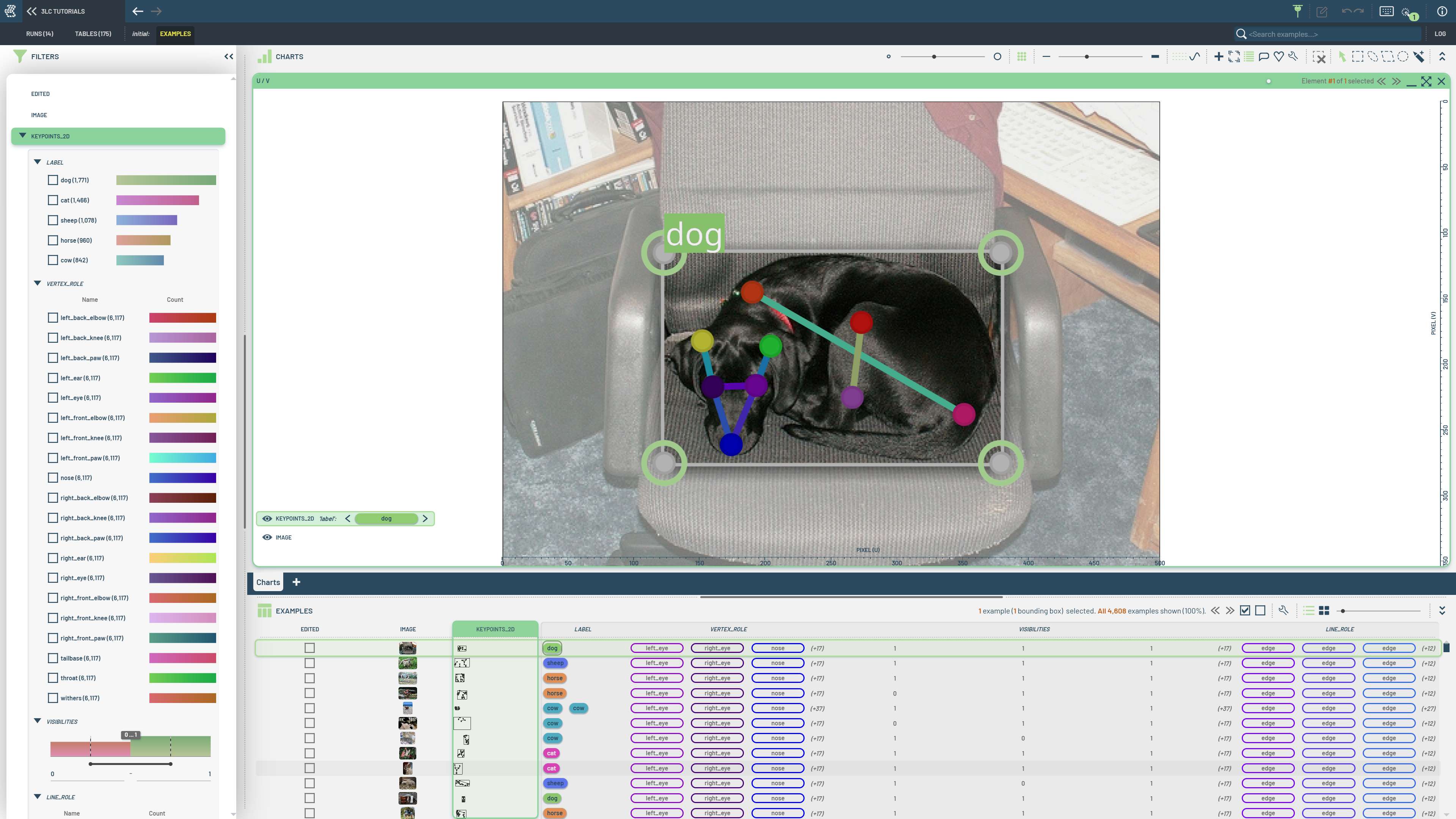
Animal pose estimation requires specialized keypoint definitions that differ from human pose datasets. Custom tables allow you to define domain-specific keypoint structures and handle non-standard annotation formats that standard loaders can’t process.
This notebook demonstrates creating a keypoints table from scratch using the Animal-Pose dataset. We manually extract COCO-like JSON annotations and convert them to 3LC keypoint format, showing how to handle custom keypoint definitions and visibility flags. The Animal Pose Dataset contains diverse animal species with specialized pose annotations from a Kaggle-hosted version with COCO-like formatting that requires manual processing to create proper 3LC keypoint structures.
Project setup¶
[ ]:
PROJECT_NAME = "3LC Tutorials - 2D Keypoints"
DATASET_NAME = "AnimalPose"
TABLE_NAME = "initial"
DOWNLOAD_PATH = "../../transient_data"
Install dependencies¶
[ ]:
%pip install 3lc
%pip install kagglehub
Imports¶
Prepare data¶
The following cell downloads the dataset from Kaggle. The dataset requires 350MB of disk space, as well as a Kaggle account.
[ ]:
import kagglehub
DATASET_ROOT = kagglehub.dataset_download("bloodaxe/animal-pose-dataset")
DATASET_ROOT = Path(DATASET_ROOT)
[ ]:
ANNOTATIONS_FILE = DATASET_ROOT / "keypoints.json"
IMAGE_ROOT = DATASET_ROOT / "images" / "images"
Load annotations / metadata¶
[ ]:
with open(ANNOTATIONS_FILE) as f:
data = json.load(f)
# Load metadata from the annotations file
NUM_KEYPOINTS = 20
KEYPOINT_NAMES = data["categories"][0]["keypoints"]
CLASSES = {cat["id"]: cat["name"] for cat in data["categories"]}
SKELETON = np.array(data["categories"][0]["skeleton"]).reshape(-1).tolist()
Some metadata is not stored in the annotations file, so we need to define it manually. These values were taken from the SuperGradients example notebook YoloNAS_Pose_Fine_Tuning_Animals_Pose_Dataset.
[ ]:
OKS_SIGMAS = [0.07] * 20
FLIP_INDEXES = [1, 0, 2, 4, 3, 6, 5, 8, 7, 10, 9, 12, 11, 14, 13, 16, 15, 17, 18, 19]
KEYPOINT_COLORS = [
[148, 0, 211],
[75, 0, 130],
[0, 0, 255],
[0, 255, 0],
[255, 255, 0],
[255, 165, 0],
[255, 69, 0],
[255, 0, 0],
[139, 0, 0],
[128, 0, 128],
[238, 130, 238],
[186, 85, 211],
[148, 0, 211],
[0, 255, 255],
[0, 128, 128],
[0, 0, 139],
[0, 0, 255],
[0, 255, 0],
[255, 69, 0],
[255, 20, 147],
]
KEYPOINT_ATTRIBUTES = [
tlc.MapElement(internal_name=kpt_name, display_color=tlc.rgb_tuple_to_hex(color))
for kpt_name, color in zip(KEYPOINT_NAMES, KEYPOINT_COLORS)
]
# A roughly drawn default pose suitable for annotating missing animals
KEYPOINTS_DEFAULT_POSE = [
[0.87, 0.22],
[0.78, 0.27],
[0.9, 0.41],
[0.83, 0.1],
[0.72, 0.13],
[0.75, 0.46],
[0.58, 0.46],
[0.29, 0.42],
[0.16, 0.4],
[0.75, 0.69],
[0.59, 0.67],
[0.29, 0.64],
[0.12, 0.63],
[0.78, 0.88],
[0.59, 0.9],
[0.3, 0.87],
[0.1, 0.87],
[0.77, 0.36],
[0.6, 0.2],
[0.25, 0.2],
]
EDGE_COLORS = [
[127, 0, 255],
[91, 56, 253],
[55, 109, 248],
[19, 157, 241],
[18, 199, 229],
[54, 229, 215],
[90, 248, 199],
[128, 254, 179],
[164, 248, 158],
[200, 229, 135],
[236, 199, 110],
[255, 157, 83],
[255, 109, 56],
[255, 56, 28],
[255, 0, 0],
]
LINE_ATTRIBUTES = [
tlc.MapElement(internal_name="edge", display_color=tlc.rgb_tuple_to_hex(color)) for color in EDGE_COLORS
]
Load the annotations¶
[ ]:
annotations = data["annotations"]
images = data["images"]
row_data = {
"image": [],
"keypoints_2d": [],
}
# Pre-compute mapping from image_id to annotations for faster lookup
image_id_2_anns = {}
for ann in annotations:
image_id_2_anns.setdefault(str(ann["image_id"]), []).append(ann)
for image_id, image_path in tqdm(images.items(), total=len(images), desc="Loading annotations"):
image_path = IMAGE_ROOT / image_path
if not image_path.exists():
print(f"Image {image_path} does not exist")
continue
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
width, height = img.size
keypoints = tlc.Keypoints2DInstances.create_empty(image_height=height, image_width=width)
for ann in image_id_2_anns[image_id]:
# Annotation file uses 0-1 visibility channel, 3LC uses COCO three-state visibility (0-1-2).
ann["keypoints"] = [[x, y, 2 if v else 0] for (x, y, v) in ann["keypoints"]]
keypoints.add_instance(
keypoints=ann["keypoints"],
bbox=ann["bbox"],
label=ann["category_id"],
)
row_data["image"].append(tlc.Url(image_path).to_relative().to_str()) # Url.to_relative applies aliases
row_data["keypoints_2d"].append(keypoints.to_row())
Create table¶
We create a Table using from_dict, specifying the attributes and metadata of the keypoints-column using a Keypoints2DSchema.
[ ]:
keypoints_schema = tlc.Keypoints2DSchema(
num_keypoints=NUM_KEYPOINTS,
classes=CLASSES,
points=KEYPOINTS_DEFAULT_POSE,
lines=SKELETON,
line_attributes=LINE_ATTRIBUTES,
point_attributes=KEYPOINT_ATTRIBUTES,
include_per_point_visibility=True,
flip_indices=FLIP_INDEXES,
oks_sigmas=OKS_SIGMAS,
)
[ ]:
table = tlc.Table.from_dict(
data=row_data,
structure={
"image": tlc.ImageUrlSchema(),
"keypoints_2d": keypoints_schema,
},
table_name=TABLE_NAME,
dataset_name=DATASET_NAME,
project_name=PROJECT_NAME,
)
Inspect the table¶
We can use the KeypointHelper class to extract various geometric information from the table.
[ ]:
table
[ ]:
# Get the oks sigmas from the table
tlc.KeypointHelper.get_oks_sigmas_from_table(table)
[ ]:
# Get the flip indices from the table
tlc.KeypointHelper.get_flip_indices_from_table(table)
[ ]:
# Get the skeleton from the table
tlc.KeypointHelper.get_lines_from_table(table)
[ ]:
# Get the keypoint attributes from the table
tlc.KeypointHelper.get_keypoint_attributes_from_table(table)
[ ]:
# Get the line attributes from the table
tlc.KeypointHelper.get_line_attributes_from_table(table)