View source
Download
.ipynb
Training a classifier using PyTorch Lightning¶
This notebooks trains a classifier on CIFAR-10 using Pytorch Lightning.
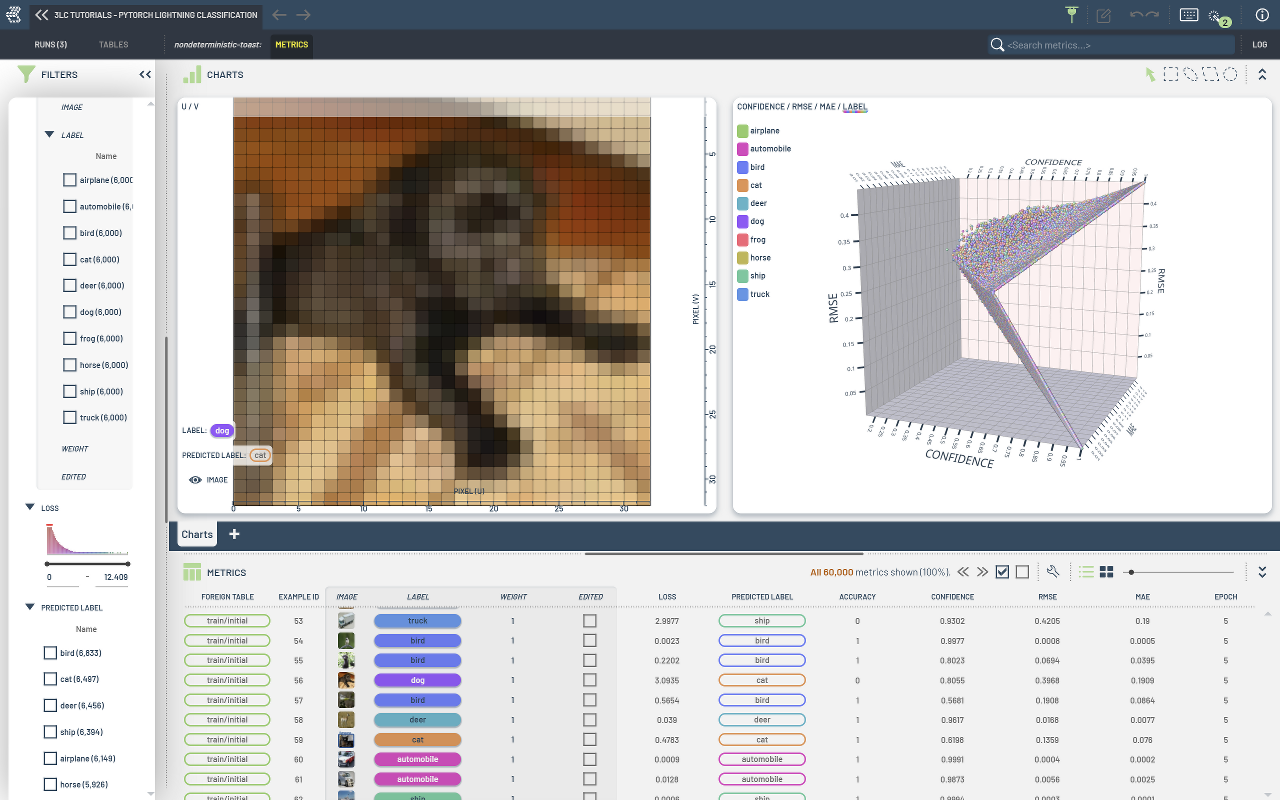
When using a LightningModule which defines the train_dataloader, val_dataloader and/or test_dataloader methods, we can decorate our LightningModule with the tlc.module_decorator to automatically generate Tables for our datasets and collect any desired metrics into a Run.
Project setup¶
[ ]:
PROJECT_NAME = "3LC Tutorials - PyTorch Lightning Classification"
RUN_NAME = "Train classifier"
RUN_DESCRIPTION = "Train a resnet model on CIFAR-10"
TMP_PATH = "../../transient_data"
EPOCHS = 5
BATCH_SIZE = 32
NUM_WORKERS = 0
Install dependencies¶
[ ]:
%pip install 3lc[pacmap]
%pip install pytorch-lightning
%pip install git+https://github.com/3lc-ai/3lc-examples.git
Imports¶
[ ]:
import pytorch_lightning as pl
import tlc
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
from tlc_tools.common import infer_torch_device
Define model creation function¶
[ ]:
# Create model for cifar10 training
def create_model():
return torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=False, num_classes=10)
Define the structure of our dataset¶
[ ]:
################## 3LC ##################
# Define the structure of a sample in the dataset(s)
# Here, the structure is a tuple, where the first element is a PIL image which we will call "Image",
# and the second element is an integer label, which maps to the given classes.
classes = ["airplane", "automobile", "bird", "cat", "deer", "dog", "frog", "horse", "ship", "truck"]
structure = (tlc.PILImage("Image"), tlc.CategoricalLabel("Label", classes=classes))
#########################################
Describe the metrics we want to collect¶
[ ]:
################## 3LC ##################
# Define a function for the metrics we want to collect
def metrics_fn(batch, predictor_output: tlc.PredictorOutput):
# tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]
labels = batch[1].to(infer_torch_device())
predictions = predictor_output.forward
num_classes = predictions.shape[1]
one_hot_labels = F.one_hot(labels, num_classes=num_classes).float()
# Confidence & Predicted
softmax_output = torch.nn.functional.softmax(predictions, dim=1)
predicted_indices = torch.argmax(predictions, dim=1)
confidence = torch.gather(softmax_output, 1, predicted_indices.unsqueeze(1)).squeeze(1)
# Per-sample accuracy (1 if correct, 0 otherwise)
accuracy = (predicted_indices == labels).float()
# Unreduced Cross Entropy Loss
cross_entropy_loss: torch.Tensor = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction="none")(predictions, labels)
# RMSE
mse: torch.Tensor = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction="none")(softmax_output, one_hot_labels)
mse = mse.mean(dim=1)
rmse = torch.sqrt(mse)
# MAE
mae: torch.Tensor = torch.nn.L1Loss(reduction="none")(softmax_output, one_hot_labels)
mae = mae.mean(dim=1)
# These values will be the columns of the Run in the 3LC Dashboard
return {
"loss": cross_entropy_loss.cpu().numpy(),
"predicted": predicted_indices.cpu().numpy(),
"accuracy": accuracy.cpu().numpy(),
"confidence": confidence.cpu().numpy(),
"rmse": rmse.cpu().numpy(),
"mae": mae.cpu().numpy(),
}
# Schemas will be inferred automatically, but can be explicitly defined if customizations are needed,
# for example to set a description or a value map for an integer label.
schemas = {
"loss": tlc.Schema(
description="Cross entropy loss",
value=tlc.Float32Value(),
),
"predicted": tlc.CategoricalLabelSchema(
display_name="predicted label",
class_names=classes,
),
}
# Use the metrics function and schemas to create a metrics collector
classification_metrics_collector = tlc.FunctionalMetricsCollector(
collection_fn=metrics_fn,
column_schemas=schemas,
)
#########################################
Define our LightningModule (With 3LC decorator)¶
[ ]:
################## 3LC ##################
@tlc.lightning_module(
structure=structure,
project_name=PROJECT_NAME,
run_name=RUN_NAME,
run_description=RUN_DESCRIPTION,
metrics_collectors=classification_metrics_collector,
)
#########################################
class MyModule(pl.LightningModule):
def __init__(self, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, lr=1e-3):
super().__init__()
self.save_hyperparameters()
self.model = create_model()
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.lr = lr
def forward(self, x):
return self.model(x)
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
x, y = batch
logits = self(x)
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, y)
return loss
def configure_optimizers(self):
return torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=self.lr)
def train_dataloader(self):
# Define transformations for the training dataset
train_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose(
[
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
]
)
# Create the training dataset, including the transformations
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root=TMP_PATH,
train=True,
download=True,
transform=train_transform,
)
# Create a DataLoader for the training dataset
return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=self.batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=NUM_WORKERS
)
def val_dataloader(self):
# Define transformations for the validation dataset
val_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose(
[
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
]
)
# Create the validation dataset, including the transformations
val_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root=TMP_PATH,
train=False,
download=True,
transform=val_transform,
)
# Create a DataLoader for the validation dataset
return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=self.batch_size, num_workers=NUM_WORKERS)
Run training¶
[ ]:
# Create the LightningModule
module = MyModule()
# Train the model
trainer = pl.Trainer(max_epochs=EPOCHS)
trainer.fit(module)
After training has completed, the Run can be viewed in the 3LC Dashboard.