Virtual Columns¶
Virtual columns are metrics derived from existing columns in the Dashboard, through applying some operation to one or more columns. Filtering and sorting on these virtual columns can give you deeper insights into your model and training set and help you find issues with your data, your model, or perhaps your entire approach to the problem at hand. The exact operations available will depend on the type of data in the selected columns. In general we can divide operations into two main categories: Global operations and Local operations. For a full list of operations, see Operations.
Creating a virtual column¶
To derive a virtual column, select one or more columns, RightClick on one of the selected columns,
hover over Derive virtual column, and select an operation to derive the virtual column.
The virtual column will be next to the input column if there is only one input column or located at the far right of the
table if there are multiple input columns. In the screenshot below, the virtual column Lossrank is
derived from a single column Loss and the virtual column RMSE/MAE is derived from a
divide operation of two columns RMSE and MAE.
Properties of virtual columns¶
Virtual columns have following properties:
Virtual columns can be derived from one or more input columns.
Virtual columns can further be derived from input virtual columns.
The available operations depend on the type of data in the input columns. For instance, the False Positives (FP) operation is only available when the BBs and BBspredicted columns are selected.
Some operations, e.g.,
divideandgroup, are order-dependent, i.e., they depend on the selection order of the input columns.Global operations, e.g.,
rankandoccurrence, calculate the results based on the context of all rows, whereas local operations, e.g.,absandsum, calculate the results on a single row basis.Virtual columns are dynamic, that is, the values of virtual columns will be automatically re-calculated if the values of the input columns change.
Virtual columns are always calcuated on the basis of the full table and not affected by filters. If you want to create a virtual column on a portion of the data, you can create a subset table and derive the virtual column there.
Some operations can be chained together such that an intermediate virtual column does not need to be created. Chained operations are indicated by an arrow next to the operation’s name. For instance, the
groupoperation can often be chained up with subsequent operations as shown in the figure below. An accumulative loss of all epochs for each sample can be calculated by selectingsumundergroup. The derived virtual column is named Lossby(Example_id, Foreign table)_sum.
Use cases¶
Below are a few examples to illustrate how virtual columns can be used and beneficial for your data analysis.
Distribution of aspect ratios¶
If the images in your dataset have a wide range of aspect ratios, you can analyze the distribution of aspect ratios with following steps.
Steps:
Derive an aspect ratio column Height/Width: Select the Height and Width columns, then select the
DivideoperationDerive a ranking column Heght/Widthrank: Select the Heght/Width column, then select the
RankoperationCreate a 2D chart of Height/Width vs Heght/Widthrank: Select the two columns and press 2
Forgetting events¶
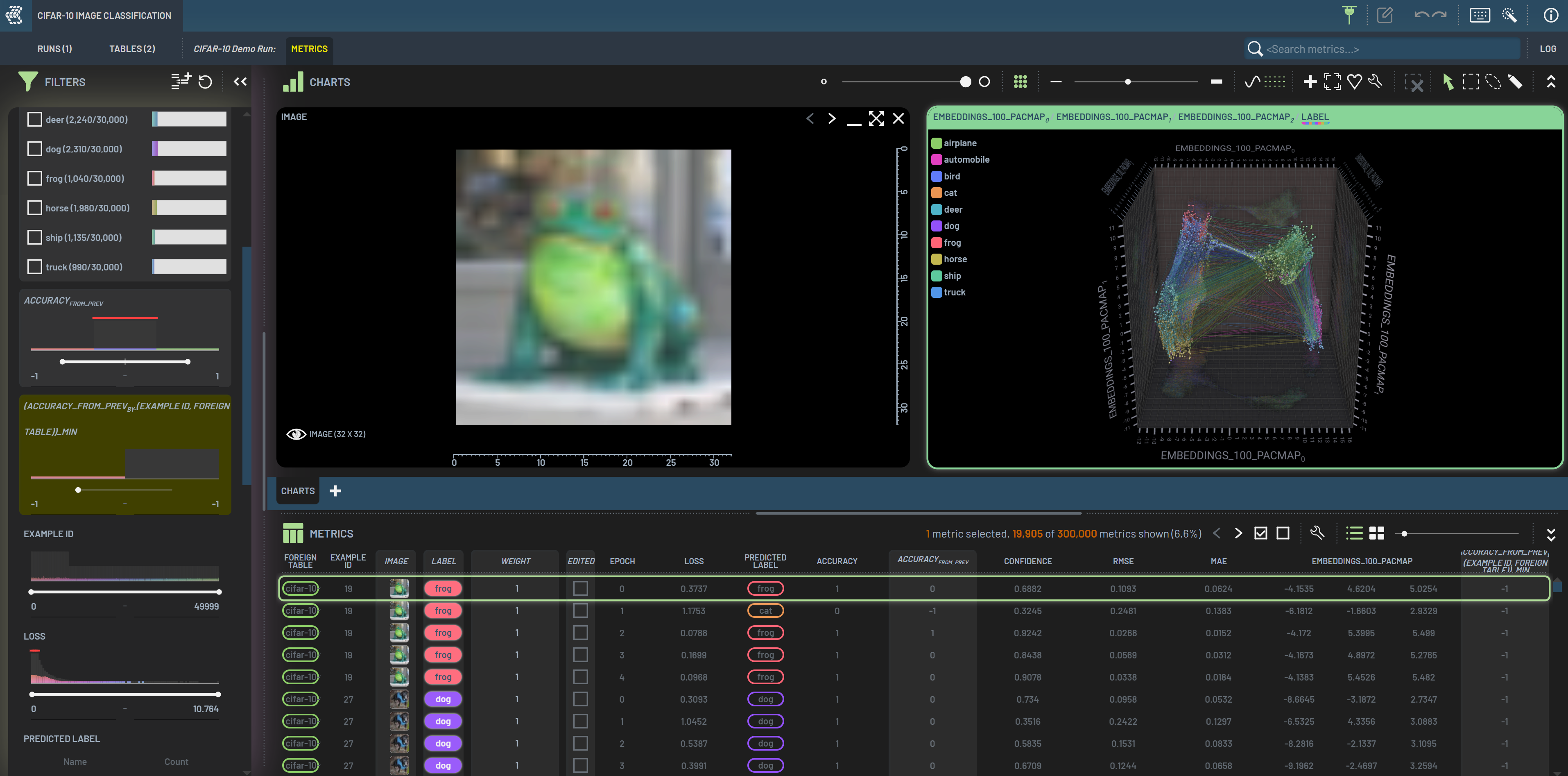
A forgetting event (FE) is defined as an correct prediction in an epoch followed by an incorrect one in the next epoch. FE-prone samples are often considered as hard ones to learn. We can find those FE-prone samples by following steps. Note: metrics of at least five epochs need to be collected to conduct this workflow.
Steps:
Derive an column of accuracy difference between an epoch and previous one: Select Accuracy, then select the
From previousoperation. This virtual column is named Accuracyfrom_prevDerive an chained
Group|Mincolumn: Select the Accuracyfrom_prev, Example_id, and Foreign table in this order, then select the chainedGroup|Minoperation. This derived column is named (Accuracy_from_prevby-(Example_id, Foreign table))_min
Filter (Accuracy_from_prevby-(Example_id, Foreign table))_min to -1. The resulted samples are those with forgetting events.
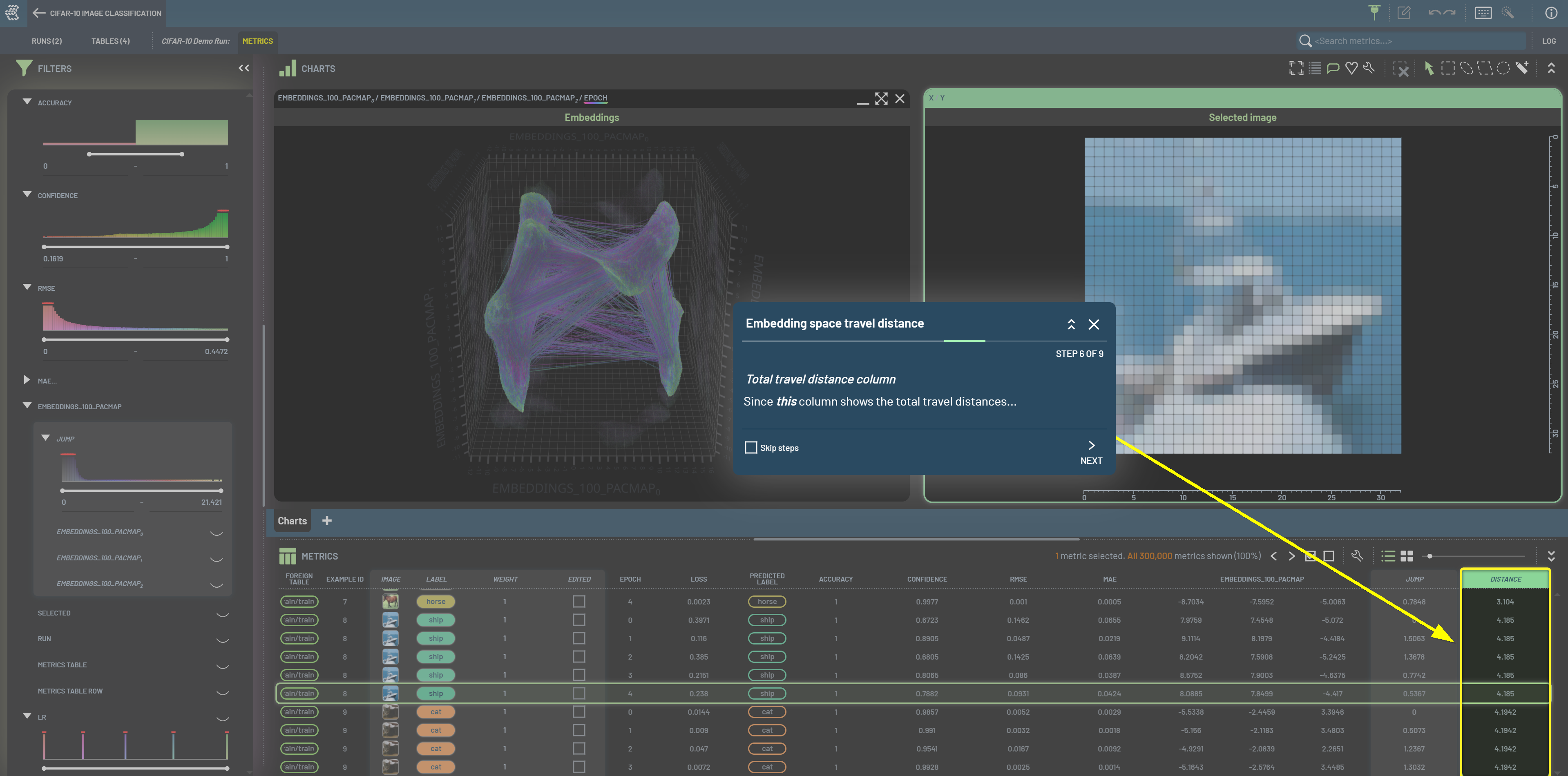
Embeddings travel distances¶
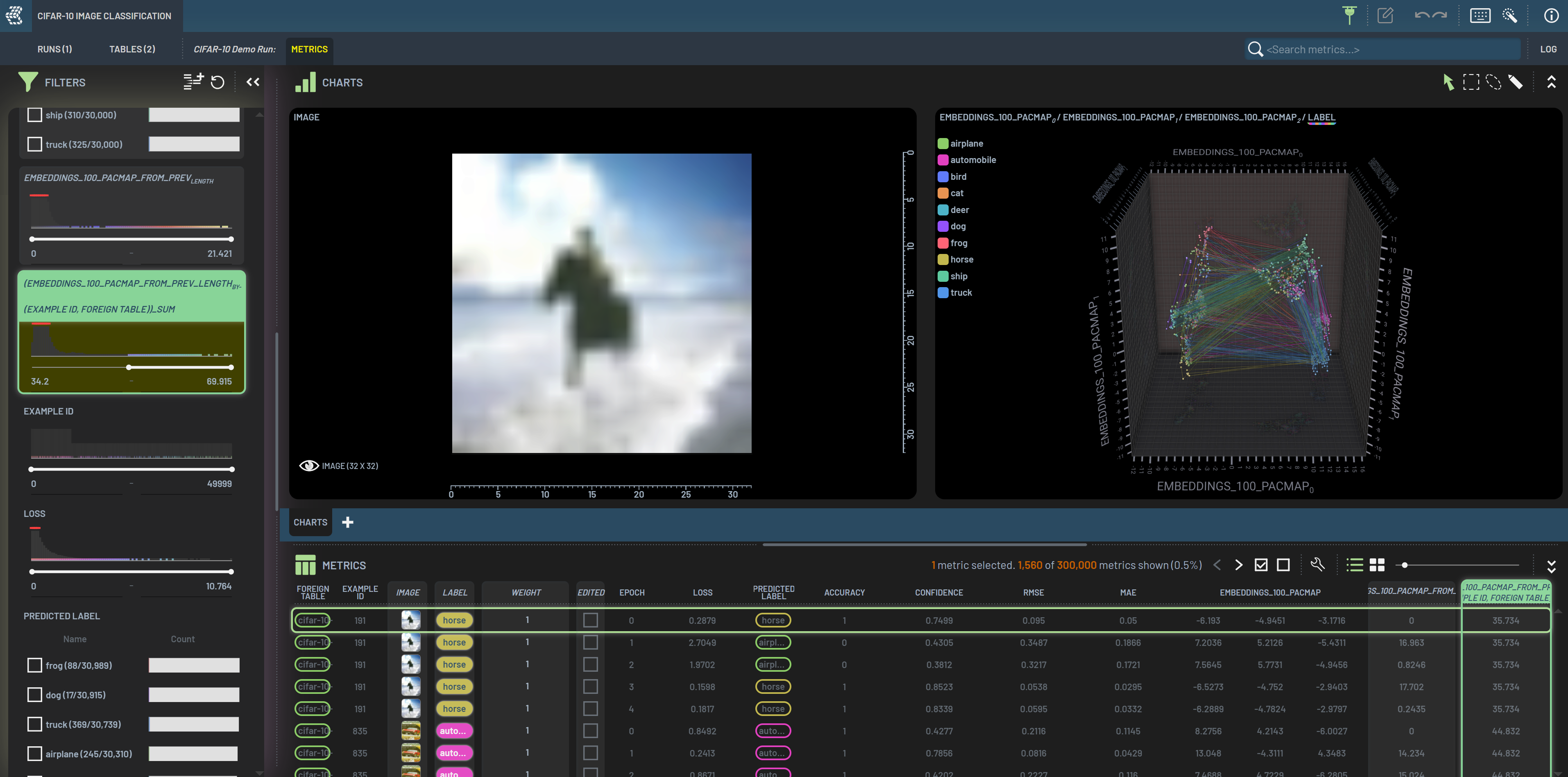
We can use this workflow to explore the samples that travel long distances in the embeddings space. Embeddings travel distances are the sum of Euclid lengths from one epoch to the next for a given sample. Long travel distances can be used as an indication of hard samples. This workflow requires embeddings collection for multiple epochs. Note that this workflow is also available in how to use workflows.
Steps:
Derive a chained
From previous|Lengthcolumn on the embeddings: select the Embeddings column, then select the chainedFrom previous|Lengthoperation. This virtual column is named Embeddings_from_prevlength.Derive a chained
Group|Sumcolumn on the theLengthvirtual column: select Embeddings_from_prevlength, Example_id, and Foreign table in this order, then select the chainedGroup|Sumoperation. The derived column is named (Embeddings_from_prev_lengthby-(Example_id, Foreign table))_sum.Filter (Embeddings_from_prev_lengthby-(Example_id, Foreign table))_sum to mid to high value range. The resulted samples are those with long embeddings travel distances.
Operations¶
The following sections describe all the available operations for creating virtual columns.
Global operations¶
Global operations need the full context of every row of its input columns to produce a result for any individual row. The Occurrences operation, which counts the number of times each value(s) occur in one or more columns, is an example of a global operation. A complete list of the available global operations, along with their input requirements, can be seen below.
Operation |
Input Type |
Output type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Traversal index |
Any |
Number |
Traversal index maximizing the walk within the input column coordinate space |
Bin |
Number |
Number |
The input value, discretized to a set number of bins |
Cluster by threshold |
Any |
Number |
Groups data points by specified distance threshold. |
Rank |
Any |
Number |
The rank of each row, as sorted by the input value(s) |
Group |
Any |
Same as input |
Group index shared by all rows with the same value(s) in the input column(s) |
Nearest neighbor |
Numbers |
Number |
Distance to closest neighbor within the input column coordinate space |
Nearest neighbors |
Numbers |
Numbers |
Links to closest neighbors within the input column coordinate space |
Group-neighbor links |
Any |
Numbers |
Links to Table rows within same group |
Zip |
Number |
Number |
Joins (‘zips’) multiple columns into a single, component column. |
Link distance |
Numbers |
Numbers |
The ‘jump’ distance of each link. |
Category |
Any |
Number |
The category of each input value (i.e. their index within a combined value map. |
Derivative |
Numbers |
Numbers |
For a numeric input column evolving over time, this operation returns the difference between the next value and the previous one, divided by two (and handling first and last values appropriately). |
Deviation |
Numbers |
Numbers |
For a numeric input column evolving over time, this operation returns the difference between a value and the average between the next and previous one. |
From previous |
Numbers |
Numbers |
For a numeric input column evolving over time, this operation returns the difference between this value and the previous one. |
To next |
Numbers |
Numbers |
For a numeric input column evolving over time, this operation returns the difference between the next value and the current one. |
Aggregate |
Numbers |
Numbers |
For a numeric input column evolving over time, this operation reports the aggregated sum at each epoch/iteration. |
Occurrence |
Any |
Number |
Number of columns with the same value(s) in the input column(s) |
Primary element |
Any |
Boolean |
Whether an element is first in a group or not |
Normalize |
Number |
Number |
Normalizes the column so that its sum is 1. |
Semantic matches (before) |
String |
Number |
How many candidates were originally matched between the wide- and the narrow-search scenarios. |
Semantic matches (after) |
String |
Number |
How many candidates are finally matched between the wide- and the narrow-search scenarios. |
Chunk-to-question links |
String |
Number |
Links to Questions referring to this Article chunk. |
Question-to-chunk links |
String |
Number |
Links to article chunks referenced by this question. |
Chunk relation |
String |
Number |
Relation between this Table row and the current selection |
Embedding distances (before) |
String |
Number |
The original distances from the question to the top-K candidates (in ND-embedding space). |
Embedding distances (after) |
String |
Number |
The final distances from the question to the top-K candidates (in ND-embedding space). |
Semantic similarities (before) |
String |
Number |
The original semantic similarities between the question and the top-K candidates from embedding space. |
Semantic similarities (after) |
String |
Number |
The final semantic similarities between the question and the top-K candidates from embedding space. |
In foreign table |
Number |
Boolean |
Whether the row is present in a foreign table |
Run constants |
Number |
Any |
The entire ‘constants’ structure of the referenced Run |
Foreign table row |
Number |
Any |
The entire row of a foreign table, as referenced by a foreign key in the input table row |
Foreign table row edited |
Number |
Boolean |
Whether the foreign table row has any pending edits |
Index |
None |
Number |
Row index within table |
Filtered index |
None |
Number |
Row index within filtered table |
Random |
None |
Number |
Random value [0..1] |
Local operations¶
Local operations only need the context of a single row to produce a result. We can further subdivide local operations into three categories: Unary operations, Order-independent operations, and Order-dependent operations.
Unary operations¶
Unary operations take a single column as input, and produce a result for each row in that column. The Character count operation, which returns the length of a string, is an example of a unary operation. A complete list of the available unary operations, along with their input requirements, can be seen below.
Operation |
Input Type |
Output type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Parse string |
String |
Number |
The input string parsed as a number. In the case of multiple numeric values being present, the last one is reported. |
PickInner[…] |
Any |
Any |
A single element picked from dimension 0 of an array. |
Pick[…] |
Any |
Any |
A single element picked from the outermost dimension of an array. |
PickProperty[…] |
Any |
Any |
A child property picked from a composite property. |
PickUnrolledProperty[…] |
Any |
Any |
A child property picked by unrulling a composite property. |
Count |
String |
Number |
The number of elements within the input array. |
Element index |
Numbers |
Numbers |
The index of each array element. |
Reverse element index |
Numbers |
Numbers |
The reverse index of each array element (i.e. 0 refers to last element in array). |
Pick random |
Any |
Any |
A random element picked from the input array (if any) |
Normalize |
Numbers |
Numbers |
The input vector in normalized form |
Abs |
Number |
Number |
The absolute value of the numeric input value |
Character count |
String |
Number |
The number of characters in the input string (including whitespace). |
Log |
Number |
Number |
The log value of the numeric input value |
Non-zero |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether the numeric input value is non-zero |
Not |
Any |
Boolean |
The boolean ‘not’ of the input value(s) |
Sign |
Number |
Number |
The sign (i.e. -1, 0, or 1) of the input value(s). |
Inverse |
Number |
Number |
The inverse (i.e. 1/x) of the input value(s). |
Raw |
Any |
Same as input |
The raw value of the input property, i.e. with value maps and/or string roles removed from the schema (recursive when required) |
Word count |
String |
Number |
The number of words in the input string |
Filename |
String |
String |
The file name from the input URL |
Zero |
Number |
Boolean |
Whether the numeric input value is zero |
Positive |
Number |
Boolean |
Whether the numeric input value is above zero |
Negative |
Number |
Boolean |
Whether the numeric input value is below zero |
In range |
Number |
Boolean |
Whether the numeric input values are within a user specified range |
In set |
Number |
Boolean |
Whether the categorical input values are part of the user specified set |
Value selected |
Any |
Boolean |
Whether the value is shared with one or more selected Table rows |
Url |
Number |
Number |
The URL defined by each input value |
Angle |
Number |
Number |
The angle of th input 2D vector |
* A |
Numbers |
Numbers |
An input value multiplied by a constant number. |
+ A |
Numbers |
Numbers |
An input value with an added constant value. |
^ A |
Numbers |
Numbers |
An input value raised to a constant power. |
Exp |
Numbers |
Numbers |
A constant value raised to a power defined by the input value. |
== |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether an input value equals a constant number. |
> |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether an input value is greater than a constant number. |
>= |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether an input value is greater than or equal to a constant number. |
< |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether an input value is less than a constant number. |
<= |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether an input value is less than or equal to a constant number. |
Token length |
String |
Number |
The number of characters in each input token. |
Overlap ratio |
List elements |
Numbers |
Quotient stating how much one bounding box is overlapped by others within an image |
Unique overlap ratio |
List elements |
Numbers |
Quotient stating how much one bounding box is uniquely overlapped by others within an image |
Rectangles (absolute) |
List elements |
Rectangles |
The rectangle geometry of the bounding box list (in absolute min/max pixel coordinates) |
Rectangles (relative) |
List elements |
Rectangles |
The rectangle geometry of the bounding box list (in min/max coordinates relative to the reference image size) |
Area |
Rectangles |
Numbers |
The area of each rectangle within the input list |
Aspect |
Rectangles |
Numbers |
The aspect (i.e. width divided by height) of each rectangle within the input list |
Width |
Rectangles |
Numbers |
The width of each rectangle within the input list |
Height |
Rectangles |
Numbers |
The height of each rectangle within the input list |
Non-maximum suppression (NMS) |
List elements |
List elements |
A bounding box list where non-maximum-suppression has been performed (with a user-specified IoU threshold) |
Angle |
Geo |
Number |
The rotation angle of each bounding box. |
Distance to origin |
Geo |
Number |
The distance to the origin (0, 0) from each bounding box. |
Area |
Geo |
Number |
The area of each bounding box. |
Aspect |
Geo |
Number |
The aspect ration (width divided by height) of each bounding box. |
Width |
Geo |
Number |
The width of each bounding box. |
Height |
Geo |
Number |
The height of each bounding box. |
Center (X) |
Geo |
Number |
The center x-position of each bounding box. |
Center (Y) |
Geo |
Number |
The center y-position of each bounding box. |
Volume |
Geo |
Number |
The volume of each 3D bounding box. |
Aspect |
Geo |
Number |
The aspect ratio of each 3D bounding box (i.e. longest edge / shortest edge). |
Week since epoch |
Datetime string |
Number |
For input datetime string, returns the week since epoch. |
Hour of day |
Datetime string |
Number |
For input datetime string, returns the hour [0..23]. |
Day of week |
Datetime string |
Number |
For input datetime string, returns the day of week. |
Milliseconds since epoch |
Datetime string |
Number |
For an input datetime string, returns the number of milliseconds since epoch. |
ConstantBool |
None |
Boolean |
A constant boolean value |
ConstantInt |
None |
Number |
A constant integer value |
ConstantFloat |
None |
Number |
A constant floating point value |
ConstantString |
None |
String |
A constant string value |
Line length |
Geo |
Numbers |
The length of each line within the input geometry |
Triangle area |
Geo |
Numbers |
The area of each triangle within the input geometry |
Order-independent operations¶
Order-independent operations take two or more columns as input, and produce a result for each row in those columns. The order of the input columns does not matter. The Sum operation, which adds two or more columns together, is an example of an order-independent operation. A complete list of the available order-independent operations, along with their input requirements, can be seen below.
Operation |
Input Type |
Output type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Sum |
Numbers |
Number |
The sum of all numeric input values |
Average |
Numbers |
Number |
The arithmetic average of the numeric input values. |
Common |
Any |
Any |
The common value within the input array (if any) |
Length |
Numbers |
Number |
The length of the input vector (i.e. the square root of the sum of squared values). |
Equal |
Any |
Boolean |
Whether all input values are equal. |
Not equal |
Any |
Boolean |
Whether some of the input values differ. |
Max |
Numbers |
Number |
The largest numeric value of all input values |
Min |
Numbers |
Number |
The smallest numeric value of all input values |
Multiply |
Numbers |
Number |
The product of all numeric input values. |
Range |
Numbers |
Number |
The absolute range (i.e. ‘max value - min value’) across all numeric input values. |
Unique |
Any |
Any |
A list of all unique input values (i.e. with duplicates removed) |
Sorted |
Numbers |
Numbers |
The input vector, sorted in ascending order |
Median |
Numbers |
Number |
The median of the input vector |
Order-dependent operations¶
Order-dependent operations take two or more columns as input, and produce a result for each row in those columns. The order of the input columns affects the results of these operations. The “Subtract” operation, which subtracts one or more columns from another, is an example of an order-dependent operation. A complete list of the available order-dependent operations, along with their input requirements, can be seen below.
Operation |
Input Type |
Output type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Divide |
Numbers |
Number |
The first value divided by the second. |
To string |
Any |
String |
The input value(s) converted to a string. In the case of multiple input columns, values are comma separated. In the case of nested input columns, the values are represented as JSON. |
Hash |
Any |
Number |
A numeric hash value calculated from all input values (including scalars, nested inputs and arrays |
Subtract |
Numbers |
Number |
The first numeric input value minus all following ones. |
Delta |
Numbers |
Number |
The difference between one column and the next (i.e. ‘next value - this value’ |
Delta angle |
Numbers |
Number |
The difference between the two input angles, full-circle symmetry taken into account. |
Delta angle (two-way) |
Numbers |
Number |
The difference between the two input angles, half-circle symmetry taken into account. |
Delta angle (four-way) |
Numbers |
Number |
The difference between the two input angles, quad-circle symmetry taken into account. |
Matched prediction (TP) |
List elements |
Boolean |
Whether each predicted element is a True Positive, i.e. has a matching ground truth instance |
Unmatched prediction (FP) |
List elements |
Boolean |
Whether each prediction is a False Positive, i.e. lacks a matching ground truth instance. |
Unmatched ground truth (FN) |
List elements |
Boolean |
Whether each ground truth instance is a False Negative, i.e. has no matching prediction |
Matched ground truth (TP) |
List elements |
Boolean |
Whether each ground truth instance is a True Positive, i.e. has a matching prediction |
List elements |
Numbers |
The |
|
List elements |
Numbers |
The |
|
Per-point OKS_matched_ground_truth |
List elements |
Numbers |
The OKS for all points within matched ground truth instances (or NaN for unmatched ones). |
Per-point OKS_matched_prediction |
List elements |
Numbers |
The OKS for all points within matched predictions (or NaN for unmatched ones). |
Precision |
List elements |
Numbers |
The Precision score calculated between the predicted and ground truth instances (considering the |
Recall |
List elements |
Numbers |
The Recall score calculated between the predicted and ground truth instances (considering the |
F1 |
List elements |
Numbers |
The F1 score calculated between the predicted and ground truth instances (considering the |
Matched value |
List elements |
Any |
The matched value for each ground truth or predicted instance (considering the |
Greater than or equal |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether each value is greater than or equal to the next. |
Greater than |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether each value is greater than the next. |
Less than or equal |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether each value is less than or equal to than the next. |
Less than |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether each value is less than the next. |
Divide (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The first value divided by the second. (element-wise) |
Subtract (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The first numeric input value minus all following ones. (element-wise) |
Delta angle (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The difference between the two input angles, full-circle symmetry taken into account. (element-wise) |
Delta angle (two-way) (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The difference between the two input angles, half-circle symmetry taken into account. (element-wise) |
Delta angle (four-way) (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The difference between the two input angles, quad-circle symmetry taken into account. (element-wise) |
Sum (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The sum of all numeric input values (element-wise) |
Average (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The arithmetic average of the numeric input values. (element-wise) |
Length (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The length of the input vector (i.e. the square root of the sum of squared values). (element-wise) |
Equal (element-wise) |
Any |
Boolean |
Whether all input values are equal. (element-wise) |
Not equal (element-wise) |
Any |
Boolean |
Whether some of the input values differ. (element-wise) |
Greater than or equal (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether each value is greater than or equal to the next. (element-wise) |
Greater than (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether each value is greater than the next. (element-wise) |
Less than or equal (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether each value is less than or equal to than the next. (element-wise) |
Less than (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether each value is less than the next. (element-wise) |
Max (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The largest numeric value of all input values (element-wise) |
Min (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The smallest numeric value of all input values (element-wise) |
Multiply (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Number |
The product of all numeric input values. (element-wise) |
Normalize (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Numbers |
The input vector in normalized form (element-wise) |
Abs (element-wise) |
Number |
Number |
The absolute value of the numeric input value (element-wise) |
Character count (element-wise) |
String |
Number |
The number of characters in the input string (including whitespace). (element-wise) |
Log (element-wise) |
Number |
Number |
The log value of the numeric input value (element-wise) |
Non-zero (element-wise) |
Numbers |
Boolean |
Whether the numeric input value is non-zero (element-wise) |
Not (element-wise) |
Any |
Boolean |
The boolean ‘not’ of the input value(s) (element-wise) |
Sign (element-wise) |
Number |
Number |
The sign (i.e. -1, 0, or 1) of the input value(s). (element-wise) |
Inverse (element-wise) |
Number |
Number |
The inverse (i.e. 1/x) of the input value(s). (element-wise) |
Zero (element-wise) |
Number |
Boolean |
Whether the numeric input value is zero (element-wise) |
Url (element-wise) |
Number |
Number |
The URL defined by each input value (element-wise) |
Angle (element-wise) |
Number |
Number |
The angle of th input 2D vector (element-wise) |