.ipynb
Load FHIBE Dataset¶
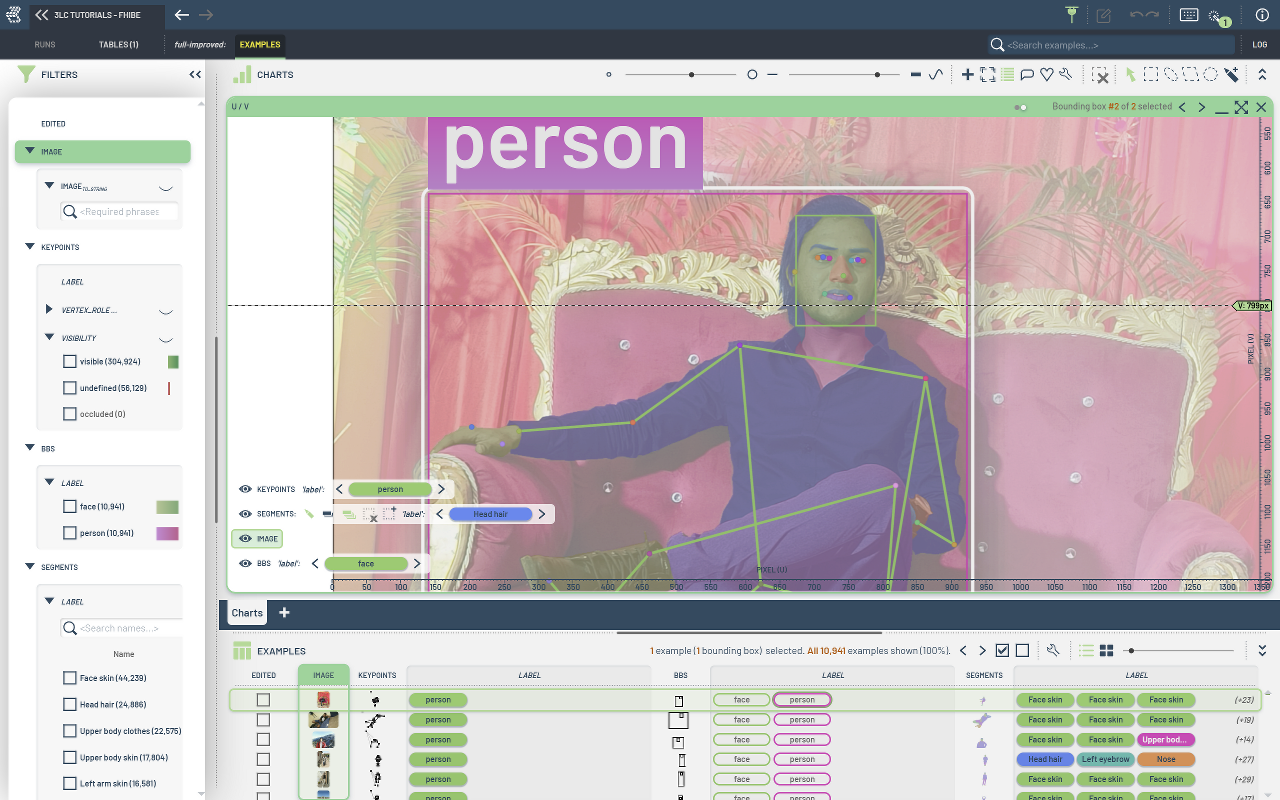
This notebook loads the Sony AI’s “Fair Human-Centric Image Benchmark” dataset as a 3LC Table, including keypoints, segmentation, bounding boxes, as well as rich subject metadata.
To download the dataset, you need to register at fairnessbenchmark.ai.sony. To read the original research paper, see here.
Several versions of the dataset exist, for this tutorial we will use version from fhibe.20250716.u.gT5_rFTA_downsampled_public.tar.gz, but the ingestion script should work for any version of the dataset, as the internal layout of the dataset is the same.
We include as much as possible of the metadata contained in the dataset, omitting only a few attributes in the name of simplicity, specifically the <attr>_QA_annotator_id fields have been left out.
The data can be categorized as follows:
Main image
Geometric annotations (instance segmentations, keypoints, facial bounding box)
Image-level metadata (shutter speed, camera manufacturer, weather conditions, etc.)
Subject-level metadata (ancestry, hair color, age, etc.)
This script reads all data from the CSV file and converts it to a format suitable for a 3LC Table. Several of the columns are stored as “categorical strings” (e.g. hair color “Blond”, “Gray”, “White”, …), these values are converted to integers, with their corresponding string values stored in the schema. This makes it easier to filter and work with these values in the 3LC Dashboard.
Install dependencies¶
[ ]:
%pip install -q 3lc
Imports¶
[ ]:
import json
import re
import time
from collections import defaultdict
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tlc
from tqdm import tqdm
Project setup¶
[ ]:
PROJECT_NAME = "3LC Tutorials - FHIBE"
DATASET_NAME = "FHIBE"
TABLE_NAME = "initial"
MAX_SAMPLES = None
DOWNLOAD_PATH = "../../transient_data"
Prepare data¶
[ ]:
FHIBE_ROOT = Path(DOWNLOAD_PATH) / "fhibe"
CSV_FILE = FHIBE_ROOT / "data/processed/fhibe_downsampled/fhibe_downsampled.csv"
if not CSV_FILE.exists():
raise FileNotFoundError(f"CSV_FILE does not exist: {CSV_FILE}")
[ ]:
# Load CSV (nrows=None reads all rows)
t0 = time.time()
df = pd.read_csv(CSV_FILE, nrows=MAX_SAMPLES)
print(f"CSV loading: {time.time() - t0:.2f}s ({len(df)} rows)")
def fast_parse(s):
"""Parse serialized Python literal using json.loads (faster than ast.literal_eval)."""
if pd.isna(s):
return s
# Replace single quotes with double quotes for JSON compatibility
# Handle escaped quotes and None values
s = s.replace("'", '"').replace("None", "null").replace("True", "true").replace("False", "false")
return json.loads(s)
# Parse columns containing serialized Python literals
SERIALIZED_COLUMNS = [
"lighting",
"weather",
"nationality",
"ancestry",
"pronoun",
"natural_hair_color",
"apparent_hair_color",
"facial_hairstyle",
"natural_facial_haircolor",
"apparent_facial_haircolor",
"natural_left_eye_color",
"apparent_left_eye_color",
"natural_right_eye_color",
"apparent_right_eye_color",
"facial_marks",
"action_subject_object_interaction",
"keypoints",
"segments",
"face_bbox",
"person_bbox",
]
t0 = time.time()
for col in SERIALIZED_COLUMNS:
if col in df.columns:
df[col] = df[col].apply(fast_parse)
print(f"Parsing serialized columns: {time.time() - t0:.2f}s")
t0 = time.time()
# Convert bounding boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x0, y0, x1, y1] format
def convert_xywh_to_xyxy(bbox):
return [bbox[0], bbox[1], bbox[0] + bbox[2], bbox[1] + bbox[3]]
df["face_bbox"] = df["face_bbox"].apply(convert_xywh_to_xyxy)
df["person_bbox"] = df["person_bbox"].apply(convert_xywh_to_xyxy)
print(f"Converting bboxes to xyxy: {time.time() - t0:.2f}s")
[ ]:
# Columns to ingest (excluding QA annotator columns and other metadata)
COLUMNS_TO_INGEST = [
# Image-level metadata
"aperture_value",
"camera_distance",
"camera_position",
"focal_length",
"iso_speed_ratings",
"lighting",
"location_country",
"location_region",
"manufacturer",
"model",
"scene",
"shutter_speed_value",
"user_date_captured",
"user_hour_captured",
"weather",
# Subject-level metadata
"subject_id",
"age",
"nationality",
"ancestry",
"pronoun",
"natural_skin_color",
"apparent_skin_color",
"hairstyle",
"natural_hair_type",
"apparent_hair_type",
"natural_hair_color",
"apparent_hair_color",
"facial_hairstyle",
"natural_facial_haircolor",
"apparent_facial_haircolor",
"natural_left_eye_color",
"apparent_left_eye_color",
"natural_right_eye_color",
"apparent_right_eye_color",
"facial_marks",
"action_body_pose",
"action_subject_object_interaction",
"head_pose",
]
# Special columns requiring custom processing (output as separate columns)
SPECIAL_COLUMNS = ["keypoints", "segments", "face_bbox"]
# Auxiliary columns (used internally but not output directly)
AUXILIARY_COLUMNS = ["person_bbox", "image_height", "image_width", "filepath"]
# Columns to treat as plain strings (not categorical due to high cardinality)
STRING_COLUMNS = ["user_date_captured", "subject_id", "location_region", "model"]
# Columns with skin color values that need display_color in schema
SKIN_COLOR_COLUMNS = ["natural_skin_color", "apparent_skin_color"]
# Threshold for auto-detecting categorical columns (max unique values)
CATEGORICAL_THRESHOLD = 100
Helper functions¶
These functions handle value cleaning, type detection, and schema inference for the categorical columns.
Value cleaning and mapping¶
[ ]:
def make_internal_name(s: str) -> str:
"""Create a valid internal name for a 3LC MapElement.
Removes numbered prefixes (like "0. Standing") and all disallowed characters.
Disallowed characters: <>\\|.:"'?*&
"""
if not isinstance(s, str):
return str(s)
# Remove numbered prefix like "0. " or "12. " (requires space after dot)
s = re.sub(r"^\d+\.\s+", "", s)
# Remove disallowed characters
for char in "<>\\|.:\"'?*&":
s = s.replace(char, "")
return s.strip()
def get_unique_values(series: pd.Series, is_list: bool = False) -> list:
"""Extract unique values from a column (already parsed from string literals)."""
if is_list:
all_vals = set()
for val in series.dropna():
if isinstance(val, list):
all_vals.update(val)
return list(all_vals)
return list(series.dropna().unique())
def sort_by_prefix(values: list) -> list:
"""Sort values by their numeric prefix if present (e.g., '0. Standing' before '1. Sitting')."""
def key(v):
match = re.match(r"^(\d+)\.\s+", str(v))
return (int(match.group(1)), str(v)) if match else (999, str(v))
return sorted(values, key=key)
def build_value_map(series: pd.Series, is_list: bool = False) -> dict[str, tuple[int, str]]:
"""Build a mapping from internal_name to (index, display_name).
The display_name is the original value, internal_name has disallowed chars removed.
Returns: {internal_name: (index, display_name), ...}
"""
unique_vals = sort_by_prefix(get_unique_values(series, is_list))
return {
make_internal_name(v): (i, v) # v is the original value for display
for i, v in enumerate(unique_vals)
}
Type detection and schema inference¶
[ ]:
def detect_column_type(col_name: str, series: pd.Series) -> str:
"""Detect the type of a column for schema inference.
Returns one of: 'numeric', 'string', 'categorical', 'categorical_list', 'special'
"""
if col_name in SPECIAL_COLUMNS:
return "special"
if col_name in STRING_COLUMNS:
return "string"
if series.dtype in ["int64", "float64"]:
return "numeric"
# Check if column contains lists (already parsed)
sample = series.dropna().iloc[0] if len(series.dropna()) > 0 else None
if isinstance(sample, dict):
return "special"
if isinstance(sample, list):
if sample and isinstance(sample[0], str):
return "categorical_list"
return "special"
# For string columns, use unique count to determine categorical vs string
return "categorical" if series.nunique() <= CATEGORICAL_THRESHOLD else "string"
def tuple2hex(t: str) -> str:
"""Convert a serialized RGB list to hex color: '[255, 255, 255]' -> '#FFFFFF'"""
nums = [int(c) for c in t.strip("[]").split(",")]
return "#{:02X}{:02X}{:02X}".format(*nums)
def build_map_elements(value_map: dict, col_name: str = None) -> dict:
"""Build MapElement dict from value_map for use in schema.
Args:
value_map: {internal_name: (index, display_name), ...}
col_name: Column name, used for special handling (e.g., skin color)
Returns: {index: MapElement, ...}
"""
elements = {}
for internal_name, (idx, display_name) in value_map.items():
kwargs = {"display_name": display_name}
# Special handling for skin color columns
if col_name in SKIN_COLOR_COLUMNS:
kwargs["display_color"] = tuple2hex(internal_name)
elements[idx] = tlc.MapElement(internal_name, **kwargs)
return elements
def infer_schema(col_name: str, series: pd.Series, default_args: dict):
"""Infer the appropriate 3LC schema for a column based on its data."""
col_type = detect_column_type(col_name, series)
is_list = col_type == "categorical_list"
if col_type == "numeric":
return tlc.Int32Schema(**default_args) if series.dtype == "int64" else tlc.Float32Schema(**default_args)
if col_type == "string":
return tlc.StringSchema(**default_args)
if col_type in ("categorical", "categorical_list"):
value_map = build_value_map(series, is_list=is_list)
map_elements = build_map_elements(value_map, col_name)
if is_list:
return tlc.CategoricalLabelListSchema(classes=map_elements, **default_args)
return tlc.CategoricalLabelSchema(classes=map_elements, **default_args)
return None # Special columns handled separately
Consolidation of country spelling variations¶
[ ]:
# Taken from https://github.com/SonyResearch/fhibe_evaluation_api/blob/main/fhibe_eval_api/datasets/fhibe.py
loc_country_name_mapping = {
"Abgola": "Angola",
"Abuja": "Nigeria",
"Argentiina": "Argentina",
"Australie": "Australia",
"Autsralia": "Australia",
"Auustralia": "Australia",
"Bahamas, The": "Bahamas",
"Caanada": "Canada",
"Canadad": "Canada",
"French": "France",
"Hanoi Vietnam": "Viet Nam",
"Ho Chi Min": "Viet Nam",
"Hong Kong": "China, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region",
"I Go": None,
"Italiana": "Italy",
"Keenya": "Kenya",
"Kenyan": "Kenya",
"Kiambu": "Kenya",
"Lagos": "Nigeria",
"Lceland": "Iceland",
"Mexican": "Mexico",
"Micronesia": "Micronesia (Federated States of)",
"Mironesi": "Micronesia (Federated States of)",
"Mironesia": "Micronesia (Federated States of)",
"Morroco": "Morocco",
"Muranga": "Kenya",
"Nairobi Nairobi": "Kenya",
"Netherlands": "Netherlands (Kingdom of the)",
"Nigerian": "Nigeria",
"Nigeriia": "Nigeria",
"Niheria": "Nigeria",
"Nugeria": "Nigeria",
"Nyari": "Kenya",
"Owow Disable Abilities Off Level Up": None,
"Pakisan": "Pakistan",
"Pakisatn": "Pakistan",
"Pakistain": "Pakistan",
"Paksitan": "Pakistan",
"Phillipines": "Philippines",
"Punjab": "Pakistan",
"South Afica": "South Africa",
"South Afria": "South Africa",
"South African": "South Africa",
"Southern Africa": "South Africa",
"South Korea": "Republic of Korea",
"Tanzania": "United Republic of Tanzania",
"Trinidad And Tobago": "Trinidad and Tobago",
"Turkey": "Türkiye",
"Ua": "Ukraine",
"Uae": "United Arab Emirates",
"Ugnd": "Uganda",
"Uk": "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland",
"United Kingdom": "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland",
"Ukaine": "Ukraine",
"United States": "United States of America",
"Usa": "United States of America",
"Venezuela": "Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of)",
"Veitnam": "Viet Nam",
"Vienam": "Viet Nam",
"Vietam": "Viet Nam",
"Vietnam": "Viet Nam",
"Vietname": "Viet Nam",
"Viietnam": "Viet Nam",
"Vitenam": "Viet Nam",
"Vitnam": "Viet Nam",
"Viwtnam": "Viet Nam",
}
def fix_location_country(country: str) -> str:
"""Format the location_country attribute string.
Some countries are misspelled or inconsistently formatted.
Args:
country: The original string annotation
Return:
The re-formatted string
"""
if pd.isna(country):
return country
if country in loc_country_name_mapping:
return loc_country_name_mapping[country]
country_fmt = country.strip().title()
if country_fmt in loc_country_name_mapping:
return loc_country_name_mapping[country_fmt]
else:
return country_fmt
# Apply normalization to DataFrame before building value maps
df["location_country"] = df["location_country"].apply(fix_location_country)
Define data processing steps¶
[ ]:
NUM_KEYPOINTS = 33
# fmt: off
KEYPOINTS = [
"Nose", # 0
"Right eye inner", # 1
"Right eye", # 2
"Right eye outer", # 3
"Left eye inner", # 4
"Left eye", # 5
"Left eye outer", # 6
"Right ear", # 7
"Left ear", # 8
"Mouth right", # 9
"Mouth left", # 10
"Right shoulder", # 11
"Left shoulder", # 12
"Right elbow", # 13
"Left elbow", # 14
"Right wrist", # 15
"Left wrist", # 16
"Right pinky knuckle", # 17
"Left pinky knuckle", # 18
"Right index knuckle", # 19
"Left index knuckle", # 20
"Right thumb knuckle", # 21
"Left thumb knuckle", # 22
"Right hip", # 23
"Left hip", # 24
"Right knee", # 25
"Left knee", # 26
"Right ankle", # 27
"Left ankle", # 28
"Right heel", # 29
"Left heel", # 30
"Right foot index", # 31
"Left foot index", # 32
]
SKELETON = [
11, 12, 11, 13, 13, 15, 12, 14, 14, 16, 12, 24, 11, 23, 23, 24,
24, 26, 26, 28, 23, 25, 25, 27, 27, 29, 29, 31, 28, 30, 30, 32,
31, 27, 32, 28, 16, 18, 15, 17, 19, 17, 18, 20, 16, 20, 15, 19, 15, 21, 16, 22,
]
# fmt: on
# Pre-build keypoint name to index mapping for fast lookup
KEYPOINT_TO_INDEX = {name: i for i, name in enumerate(KEYPOINTS)}
def build_segments_value_map(df: pd.DataFrame) -> dict[str, int]:
"""Build value map for segment classes from the DataFrame."""
all_classes = set()
for segments in df["segments"].dropna():
for seg in segments:
all_classes.add(seg["class_name"])
sorted_classes = sort_by_prefix(list(all_classes))
return {make_internal_name(c): i for i, c in enumerate(sorted_classes)}
# Build segments value map from data
segments_value_map = build_segments_value_map(df)
def process_keypoints(keypoints: dict, person_bbox: list, image_width: int, image_height: int):
"""Convert keypoints to 3LC format.
Args:
keypoints: Dict mapping keypoint names to [x, y, visibility] values
person_bbox: Bounding box in [x0, y0, x1, y1] format (already converted)
image_width: Image width in pixels
image_height: Image height in pixels
"""
kpts_arr = np.zeros((NUM_KEYPOINTS, 3), dtype=np.float32)
for kpt_name, (x, y, viz) in keypoints.items():
idx = KEYPOINT_TO_INDEX.get(make_internal_name(kpt_name))
if idx is not None:
kpts_arr[idx, :] = [x, y, 2 if viz else 0]
instances = tlc.Keypoints2DInstances.create_empty(
image_width=image_width,
image_height=image_height,
include_keypoint_visibilities=True,
include_instance_bbs=True,
)
instances.add_instance(keypoints=kpts_arr, label=0, bbox=person_bbox)
return instances.to_row()
def process_segments(segments: list, image_width: int, image_height: int):
"""Convert segments to 3LC format."""
def group_segments_by_class(segments):
grouped: dict[str, list[list]] = defaultdict(list)
for segment in segments:
class_name = make_internal_name(segment["class_name"])
poly = [[p["x"], p["y"]] for p in segment["polygon"]]
flattened = [coord for point in poly for coord in point]
grouped[class_name].append(flattened)
return grouped
masks, labels = [], []
for class_name, polygons in group_segments_by_class(segments).items():
mask = tlc.SegmentationHelper.mask_from_polygons(polygons, image_height, image_width)
masks.append(mask)
labels.append(segments_value_map[class_name])
return tlc.SegmentationMasksDict(
image_width=image_width,
image_height=image_height,
masks=np.stack(masks, axis=-1),
instance_properties={"label": labels},
)
def process_face_bbox(face_bbox: list, image_width: int, image_height: int):
"""Convert face bounding box to 3LC format.
Args:
face_bbox: Bounding box in [x0, y0, x1, y1] format (already converted)
"""
return {
tlc.IMAGE_WIDTH: image_width,
tlc.IMAGE_HEIGHT: image_height,
tlc.BOUNDING_BOX_LIST: [
{
tlc.X0: face_bbox[0],
tlc.Y0: face_bbox[1],
tlc.X1: face_bbox[2],
tlc.Y1: face_bbox[3],
tlc.LABEL: 0,
}
],
}
[ ]:
def convert_value(value, col_name: str, value_maps: dict):
"""Convert a raw value to the format expected by 3LC.
For categorical columns, maps string values to integer indices.
For list columns, maps each value in the list.
"""
# Handle NaN values for scalar types - convert to None for proper handling
if not isinstance(value, (list, dict)) and pd.isna(value):
return None
col_type = detect_column_type(col_name, df[col_name])
if col_type == "numeric":
return value
if col_type == "string":
return value
if col_type == "categorical_list":
value_map = value_maps.get(col_name)
if value_map is None:
return value
return [value_map[make_internal_name(v)][0] for v in value] # [0] gets the index
if col_type == "categorical":
value_map = value_maps.get(col_name)
if value_map is None:
return value
return value_map[make_internal_name(value)][0] # [0] gets the index
return value
[ ]:
# Build value maps for all categorical columns
value_maps = {}
for col_name in COLUMNS_TO_INGEST:
col_type = detect_column_type(col_name, df[col_name])
if col_type in ("categorical", "categorical_list"):
is_list = col_type == "categorical_list"
value_maps[col_name] = build_value_map(df[col_name], is_list=is_list)
print(f"Built value maps for {len(value_maps)} categorical columns")
Row processing¶
This function processes a single DataFrame row, converting it to the format expected by the TableWriter.
[ ]:
def process_row(csv_row):
"""Process a single CSV row into the format expected by 3LC."""
image_width = int(csv_row["image_width"])
image_height = int(csv_row["image_height"])
# Build absolute image path and convert to relative 3LC URL
image_path = FHIBE_ROOT / csv_row["filepath"]
image_url = tlc.Url(image_path).to_relative().to_str()
# Build the output row with special columns
row = {
"image": image_url,
"keypoints": process_keypoints(csv_row["keypoints"], csv_row["person_bbox"], image_width, image_height),
"segments": process_segments(csv_row["segments"], image_width, image_height),
"face_bbox": process_face_bbox(csv_row["face_bbox"], image_width, image_height),
}
# Add all other columns with appropriate conversions
for col_name in COLUMNS_TO_INGEST:
if col_name in SPECIAL_COLUMNS:
continue
row[col_name] = convert_value(csv_row[col_name], col_name, value_maps)
return row
Define column schemas¶
We are now ready to define our schemas.
[ ]:
# Default schema args: hidden by default and read-only in UI
default_schema_args = {"default_visible": False, "writable": False}
# Build schemas for special columns
special_schemas = {
"image": tlc.ImageUrlSchema(),
"keypoints": tlc.Keypoints2DSchema(
classes=["person"],
num_keypoints=NUM_KEYPOINTS,
lines=SKELETON,
point_attributes=KEYPOINTS,
include_per_point_visibility=True,
),
"face_bbox": tlc.BoundingBoxListSchema(
label_value_map={0: tlc.MapElement("face")},
include_segmentation=False,
),
"segments": tlc.SegmentationSchema(
label_value_map={v: tlc.MapElement(k) for k, v in segments_value_map.items()},
sample_type=tlc.InstanceSegmentationMasks.sample_type,
),
}
# Infer schemas for all other columns
inferred_schemas = {}
for col_name in COLUMNS_TO_INGEST:
if col_name in SPECIAL_COLUMNS:
continue
schema = infer_schema(col_name, df[col_name], default_schema_args)
if schema is not None:
inferred_schemas[col_name] = schema
# Combine all schemas
schemas = {**special_schemas, **inferred_schemas}
print(f"Built schemas for {len(schemas)} columns")
Preview a sample row¶
Before writing all rows, let’s preview a single row to verify the data looks correct.
[ ]:
# Preview the first row
sample_row = process_row(df.iloc[0])
print(f"Sample row keys ({len(sample_row)}): {list(sample_row.keys())[:10]}...")
print(f"\nImage: {sample_row['image']}")
print(f"Subject ID: {sample_row['subject_id']}")
print(f"Age: {sample_row['age']}")
print(f"Scene: {sample_row['scene']}")
print(f"Segments keys: {list(sample_row['segments'].keys())}")
Write the Table¶
Finally, we create a TableWriter, and add our rows to the Table.
[ ]:
table_writer = tlc.TableWriter(
table_name=TABLE_NAME,
dataset_name=DATASET_NAME,
project_name=PROJECT_NAME,
column_schemas=schemas,
)
for csv_row in tqdm(df.to_dict("records"), desc="Writing rows"):
table_writer.add_row(process_row(csv_row))
table = table_writer.finalize()